FGL Gay-Lussac Federation: A Union of 20 Top Chemical Engineering Schools in France

The Fédération Gay-Lussac (FGL), or Gay-Lussac Federation, was established in 1994 and consists of 20 leading French engineering schools specializing in chemistry and chemical engineering. These prestigious institutions are dedicated to training elite professionals and conducting cutting-edge research in the field.
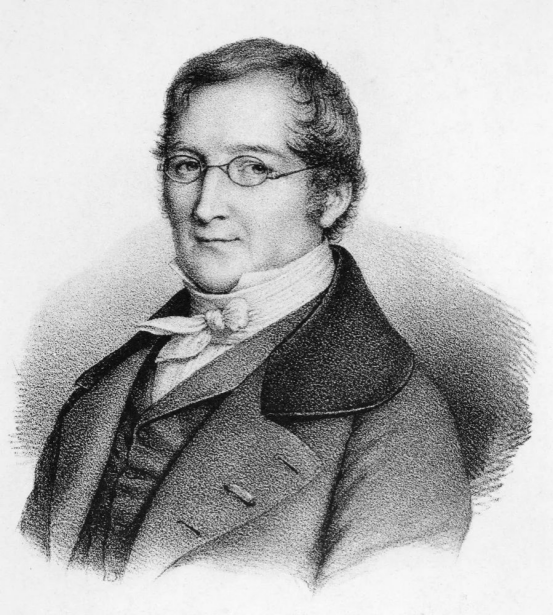
The federation is named after the renowned 18th-century French physicist and chemist Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac.
Gay-Lussac was the first to discover the law of combining volumes of gases, invented new methods for preparing alkali metals such as potassium and sodium, and went on to discover new elements like boron and iodine. His groundbreaking contributions had a tremendous impact on chemistry, helping to establish France as the world's leading scientific center at the time.

The Chemical Engineering program follows a comprehensive training model composed of four key components:
· 61% Core Professional Courses (including theoretical courses and practical courses)
· 20% Individual Projects (including experimental projects, internships, and theses)
· 11% Other Related Courses (including humanities and social sciences, quality, safety, and sustainable development)
· 8% Language Courses (mandatory or elective courses in multiple languages such as English, French, and German)
Among them, the core courses are mainly divided into eight major categories:
Analytical Chemistry, Physical Chemistry, Organic Chemistry & Polymers, Biochemistry & Biological Chemistry, Inorganic Chemistry & Materials, Chemical Engineering, Physics, and Process Simulation.
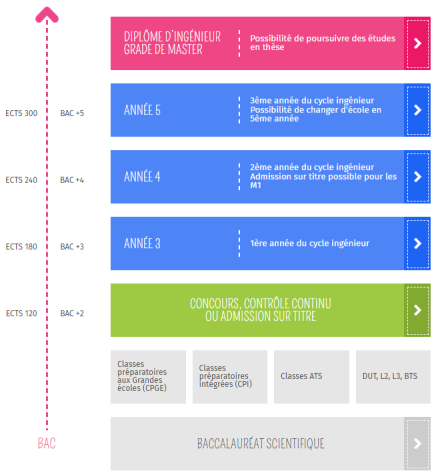
The FGL engineering program has a duration of three years (Bac+3 to Bac+5), leading to the Master’s degree in Engineering upon graduation.
International Preparatory Program – International Classes - Chem.I.St
The FGL Federation offers two types of preparatory programs for high school graduates: the "classic" preparatory program and the international preparatory program.
These programs are offered at five locations in France: Clermont-Ferrand, Lille, Nancy, Rennes, and Strasbourg.
After completing the two-year preparatory program, students can enter one of the 20 member schools without needing to take a competitive exam (admission is based on graduation ranking and continuous assessment).

Five schools within the FGL Federation offer their own preparatory programs: CPE Lyon, ENSCMu, ESCOM Compiègne, INSA Rouen, and ITECH Lyon.
Additionally, ENSIC and ENSIACET can be accessed through preparatory programs offered by the three National Polytechnic Institutes (INP).
ENSCBP Bordeaux and ENSGTI Pau recruit students from preparatory classes at the University of Bordeaux.
INSA Rouen and Centrale Marseille offer undergraduate programs.
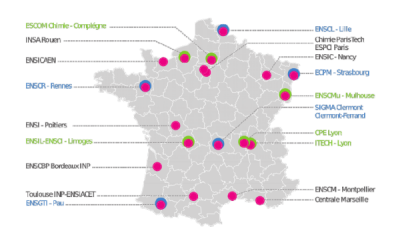
1. ENSCL - Lille
The École Nationale Supérieure de Chimie de Lille (ENSCL) was founded in 1894 and has over 4,000 graduates.
It is a public engineering school that offers multidisciplinary training in chemistry.
The school focuses on developing expertise in:
· Chemistry and materials science
· Formulation
· Chemical and sustainable processes
· Catalysis
Additionally, students gain skills in languages, social sciences, management, and project management.

2. Centrale Marseille
Founded in 1891, Centrale Marseille is a public, multidisciplinary engineering school located in Marseille.
It is one of the five prestigious Centrale engineering schools in France.
The first two years follow a general engineering curriculum, where students study:
· Mechanical engineering
· Pure and applied mathematics
· Computer science
· Optical physics
· Signal processing
· Microcontrollers
· Chemistry and chemical engineering

3. Chimie ParisTech
Founded in 1896, Chimie ParisTech is a leading French engineering school in chemistry, located in the 5th arrondissement of Paris.
It is a member of ParisTech and the PSL University (Paris Sciences & Lettres).
Key Figures:
· 350 engineering students
· 100 graduates per year
· 20% international students
· 100% employment rate for graduates

4. CPE Lyon
The École Supérieure de Chimie Physique Électronique de Lyon (CPE Lyon) was founded in 1994 following the merger of two prestigious schools:
· ESCIL (École Supérieure de Chimie Industrielle de Lyon)
· ICPI (Institut de Chimie Physique Industrielle)
Key Facts:
· Three alumni have won the Nobel Prize
· The school has numerous research collaborations with:
o CNRS (French National Research Center)
o Université Claude Bernard Lyon 1
o Université Jean Monnet (Saint-Étienne)
o Centrale Lyon
o INSA Lyon

5. ECPM - Strasbourg
The École Européenne de Chimie, Polymères et Matériaux (ECPM) was founded in 1919 and is affiliated with the University of Strasbourg.
Key Figures:
· Over 4,000 graduates
· 100 engineering students per class
· 40 teacher-researchers
· 6 affiliated research laboratories
· 45% of the scientific curriculum takes place in industrial settings
· 8 double-degree programs
· 71% of graduates find employment abroad

6. ENSCBP Bordeaux INP
The École Nationale Supérieure de Chimie, de Biologie et de Physique (ENSCBP) was founded in 1891 and is part of Bordeaux INP.
It offers five engineering programs in chemistry, physics, and agri-food sciences.
Key Figures:
· 600 engineering students
· 60 professors and faculty members
· 100 PhD students
· 8 research laboratories

7. ENSCM - Montpellier
The École Nationale Supérieure de Chimie de Montpellier (ENSCM) was founded in 1889, making it the second-oldest chemical engineering school in France.
Key Facts:
· Offers a general chemistry engineering degree
· Provides 7 elective specialization courses
Tuition fees: approximately €600 per year

8. ENSCMu - Mulhouse
The École Nationale Supérieure de Chimie de Mulhouse (ENSCMu) was founded in 1822, making it the first chemical engineering school in France.
It is affiliated with the Université de Haute-Alsace.
Programs cover:
· Analytical chemistry
· Organic chemistry
· Inorganic chemistry
· Physical chemistry
· Formulation
· Materials and polymers
· Safety and sustainable development

9. ENSCR - Rennes
The École Nationale Supérieure de Chimie de Rennes (ENSCR) was founded in 1919.
Key Figures:
· 510 engineering students
· 80 to 90 graduates per year
· More than 3,580 alumni
· 40 professors, researchers, and faculty members
· 45 PhD and postdoctoral students
· 5 patents filed each year

10. ENSGTI - Pau
The École Nationale Supérieure en Génie des Technologies Industrielles (ENSGTI) was founded in 1991 and is affiliated with the University of Pau.
It is a member of Bordeaux INP.
Specializations include:
· Process engineering
· Energy engineering
· Electrical engineering
· Industrial computing
The school aims to train future engineers with strong technical expertise, an open mindset, and a sense of responsibility.

11. ENSI - Poitiers
The École Nationale Supérieure d’Ingénieurs de Poitiers (ENSI Poitiers) was founded in 1969 and is affiliated with the University of Poitiers.
It is also a partner institution of Bordeaux INP.
Location:
ENSI Poitiers is situated in the eastern part of the University of Poitiers campus, just 13 minutes by bus from the city center.

12. ENSIC - Nancy
The École Nationale Supérieure des Industries Chimiques (ENSIC) was founded in 1887 and is part of the University of Lorraine.
It is considered one of Europe's leading schools in chemical and process engineering.
Degrees offered:
· Chemical Industrial Engineering (I2C)
· Industrial Technology Engineering (FITI)
· Also offers Master's, PhD, and professional education programs.

13. ENSICAEN - Caen
The École Nationale Supérieure d'Ingénieurs de Caen (ENSICAEN) was founded in 1976 and has grown into one of the most prestigious engineering schools in Normandy.
Key Figures:
· 51 research professors
· 27 staff members
· 780 students
· 5 PhD students
· 8,500 graduates since 1976
· 240 graduates per year
· 90 international agreements
· 6 postdoctoral researchers

14. ENSIL-ENSCI - Limoges
The École Nationale Supérieure d’Ingénieurs de Limoges (ENSIL) and the École Nationale Supérieure de Céramique Industrielle (ENSCI) merged in 2017 to form ENSIL-ENSCI.
Historical Background:
· ENSIL was founded in 1991 and is accredited by the CTI (Commission des Titres d'Ingénieur).
o Specializations: Water & Environment, Electronics & Telecommunications, Materials, and Mechatronics.
· ENSCI was established in 1893, initially focusing on ceramic arts before evolving into an industrial ceramics and materials engineering school.
o It relocated to Limoges in 1979.

15. ESCOM Chimie - Compiègne
The École Supérieure de Chimie Organique et Minérale (ESCOM Chimie) was founded in 1957.
It offers:
· A 5-year engineering program in chemistry
· A 3-year bachelor's degree program
Location:
ESCOM is located on the campus of the University of Technology of Compiègne (UTC), which has over 4,000 students.

16. ESPCI Paris
The École Supérieure de Physique et de Chimie Industrielles de la Ville de Paris (ESPCI Paris) was founded in 1882 by the Paris City Council.
It is a member of ParisTech and PSL University (Paris Sciences & Lettres).
Notable Alumni & Awards:
· 5 Nobel Prize winners from ESPCI:
o Pierre and Marie Curie
o Frédéric Joliot-Curie
o Pierre-Gilles de Gennes
o Georges Charpak
ESPCI is globally recognized for its excellence in physics, chemistry, and materials engineering.

17. INSA - Rouen
The Institut National des Sciences Appliquées de Rouen (INSA Rouen) was founded in 1985.
It is part of the INSA Group and is affiliated with the University of Normandy.
Campuses:
· Mont-Saint-Aignan, where most courses are held
· Technopôle du Madrillet, dedicated to research and innovation
Key Figures:
· 1,704 students
· 120 research faculty members
· 190 PhD students across 12 research laboratories
Engineering Specializations:
1. Chemistry
2. Energy & Propulsion
3. Information Systems
4. Applied Mathematics & Engineering
5. Mechanical Engineering & Industrial Risk Management

18. ITECH - Lyon
The Institut Textile et Chimique de Lyon (ITECH Lyon) was founded in 1899 following the merger of ESITL and EFT.
Key Figures:
· 500+ students
· 4,000+ graduates
· 16 research professors, including 9 PhD holders
Specializations:
1. Formulation Chemistry (paints, inks, adhesives, and cosmetics)
2. Textile Materials
3. Plastic Materials
4. Leather Industry

19. SIGMA Clermont - Clermont-Ferrand
The École SIGMA Clermont was created in 2016 following the merger of:
· The Institut Français de Mécanique Avancée (IFMA), founded in 1991
· The École Nationale Supérieure de Chimie de Clermont-Ferrand (ENSCCF), founded in 1908
Affiliations:
· Under the Ministry of Higher Education, Research, and Innovation
· Member of the Grenoble INP network

20. Toulouse INP-ENSIACET
The École Nationale Supérieure des Ingénieurs en Arts Chimiques et Technologiques (ENSIACET) was founded in 2001, after the merger of:
· The École Nationale Supérieure de Chimie de Toulouse (ENSCT)
· The École Nationale Supérieure d’Ingénierie Chimique (ENSIGC)
Key Figures:
· 200 students in preparatory programs
· 650 engineering students
· 170 PhD students enrolled in 4 doctoral schools
· 100 professors and researchers
· 100 administrative and technical staff members
ENSIACET specializes in chemical and process engineering and offers extensive research and industrial partnerships.
Previous article:This is already the first article Next article:This is already the last article
Return to List-
 Audencia Business School
Audencia Business School
2025-03-07
-
 NEOMA Business School
NEOMA Business School
2025-03-07
-
 SKEMA Business School
SKEMA Business School
2025-03-07
-
 EMLYON Business School
EMLYON Business School
2025-03-07

 Cn
Cn En
En Fr
Fr